UX Design - Mentor & Author.
17 Apr, 2024

In the ever-evolving landscape of digital design, Product Designers and UX Designers are crucial for user-friendly digital products. Although these two roles are closely related and often overlap, they each have distinct focuses within the product development processThis article compares UX and Product Designers, highlighting their unique roles in design and innovation. Let’s embark on this journey to unravel the intricate roles of UX Designers and Product Designers.
Defining the Roles:
UX Designer: A UX Designer is primarily concerned with creating a seamless and enjoyable user experience. This includes understanding user needs, conducting usability testing, and designing intuitive user interfaces. A UX Designer is deeply involved in the iterative process of designing and refining the user journey.
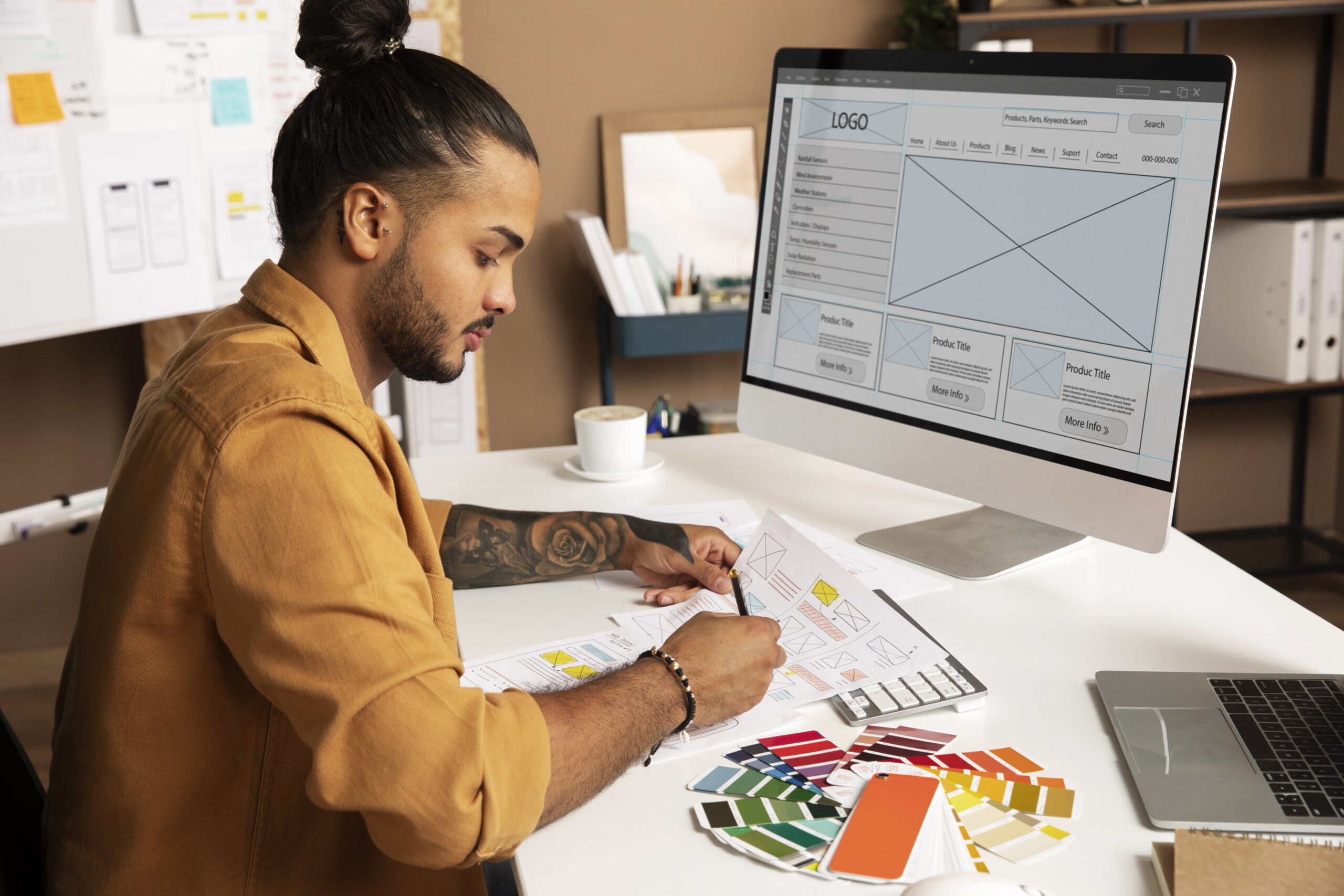

Product Designer: On the other hand, a Product Designer takes a more holistic approach to product development. Beyond the user experience, they also consider business objectives, market trends, and technical feasibility. A Product Designer is responsible for shaping the overall product vision and ensuring that it aligns with the organization’s goals.
Similarities Between Product Designers and UX Designers
Product and UX Designers collaborate closely, utilizing the design thinking process. They empathize with users, define problems, ideate solutions, prototype, test, and iterate on designs together.
Secondly, they adopt a user-centered approach, ensuring that their designs prioritize user satisfaction and address user pain points. This involves understanding user behavior, preferences, and motivations to create intuitive and engaging user experiences. Both emphasize collaboration, often working closely with cross-functional teams like developers, marketers, and stakeholders to align the final product with business goals and user needs.
Both use design tools like Figma, Sketch, Adobe XD, and InVision to create wireframes, prototypes, and mockups, facilitating effective visualization and communication of design concepts.
Differences Between Product Designers and UX Designers
Though Product Designers and UX Designers share many similarities, their roles diverge in several key aspects:
Scope of Work: Product Designers are typically responsible for the entire design process of a product, including ideation, UX, project management, and business-related processes. In contrast, UX Designers have a narrower focus, concentrating specifically on refining the user experience of a product.
Business Orientation: Product Designers often have a more business-oriented perspective, being more aware of business priorities than UX Designers. They frequently work closely with business or product teams to ensure business needs are met in the final product.
Leadership Role Product Designers lead the design process, overseeing teams including UX and visual designers, researchers, and business teams. On the other hand, UX Designers generally have a more hands-on approach to designing user-friendly products.
Design Execution: While both roles involve creating prototypes to visualize and test design solutions, UX Designers typically focus more on designing the actual visual and interactive elements of a product, often involving tasks like wireframing, user journey mapping, and creating mockups.
Specialization: Product Designers are versatile, handling UX, UI, project management, and problem-solving. UX Designers specialize in creating intuitive user experiences, prioritizing usability, accessibility, and user-centric design.
Skills Required for UX Designers
User-Centered Design: Understanding and applying user-centered design principles is foundational to the role of a UX Designer. They should be able to empathize with users, understand their needs and preferences, and create solutions that address these effectively.
Prototyping and Wireframing: Proficiency in creating wireframes and prototypes using tools like Figma, Sketch, or Adobe XD is crucial for UX Designers. This allows them to visualize and communicate design concepts and iterate based on user feedback.
Usability Testing: Conducting usability tests and gathering feedback from users is a vital skill for UX Designers. They should be able to design and execute these tests, analyze the results, and make informed design decisions based on the findings.
Research and Analysis: Strong research skills are essential for UX Designers to gather insights into user behavior, market trends, and competitor analysis. They should be able to synthesize this information and apply it to their designs.
Interaction Design: UX Designers need to design intuitive and engaging user interactions for digital products. This involves creating clear user flows, information architecture, and navigation that enhance the user experience.
Skills Required for Product Designers
Product Management: Product Designers need to have a strong understanding of product management principles to lead the design process effectively. This includes defining product strategies, creating roadmaps, and managing the product life cycle.
UX/UI Design: While UX Designers focus more on the user experience, Product Designers need to have a solid understanding of both UX and UI design principles. This includes creating intuitive user interfaces and designing user interactions.
Problem-Solving: Product Designers must excel in problem-solving, understanding user needs, and crafting innovative solutions to address them efficiently.
Business Acumen: Product Designers need to grasp business goals, market trends, and customer needs to design products aligned with both user satisfaction and business strategy.
Technical Skills: While not necessarily required to code, Product Designers should have a general understanding of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to communicate effectively with developers and ensure the feasibility of their designs.
Conclusion
In this article, we explored the key differences and similarities between UX designers and product designers, along with the essential skill sets required for both roles. I hope this has provided you with a clear understanding of the distinct paths available in design. If torn between UX and product design, prioritize what brings you the most satisfaction and aligns with your values. Remember, both roles offer fulfilling and exciting career opportunities, and choosing the right path is essential for your professional growth. Wishing you all the best on your design journey!